Introduction to Trigonometry
What is Trigonometry?
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the relationship between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. It is especially useful in measuring heights, distances, and angles in real-world contexts like construction, navigation, and astronomy.
Right-Angled Triangle and Its Sides In a right-angled triangle, one of the angles is exactly 90°. The three sides of the triangle are:
| Side | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Perpendicular | 𝑝 | The side opposite to the angle being considered (not the right angle) |
| Base | 𝑏 | The side adjacent to the angle being considered (not the hypotenuse) |
| Hypotenuse | ℎ | The side opposite the right angle; the longest side in a right triangle |
In a right-angled triangle

Figure 1: Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse in a triangle.
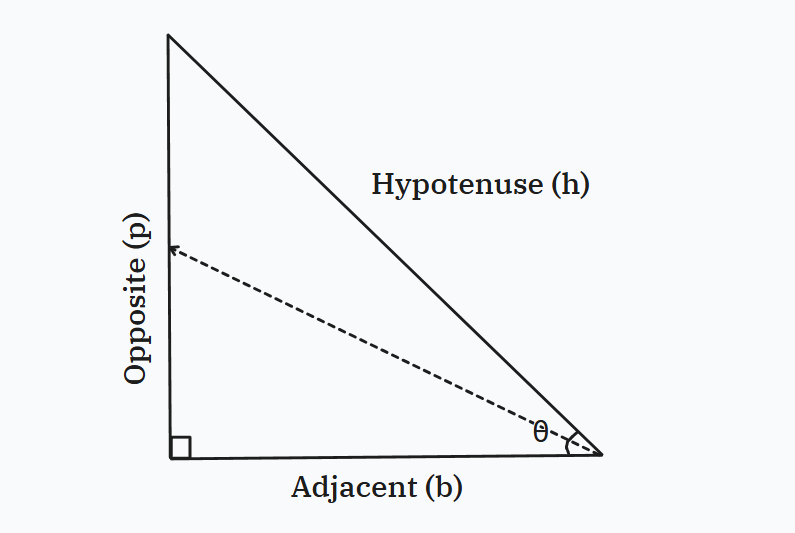
Figure 2: Relations of p, b and h with theta (θ)
Trigonometric Ratios
For a right-angled triangle with angle 𝜃, the basic trigonometric ratios are:
📐 Trigonometric Ratios Table (Standard Angles)
| Not defined |
📐 Trigonometric Ratios – Standard Angles
| Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not defined |