Introduction to Geometry
Triangle
Definition
A triangle is a closed figure formed by three line segments. It has:
-
3 sides
-
3 angles
-
3 vertices
Properties of a Triangle
-
Angle Sum Property:
The sum of interior angles of any triangle is always:

Figure 1: Triangle with sides and angles.
-
Exterior Angle Property:
An exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles:
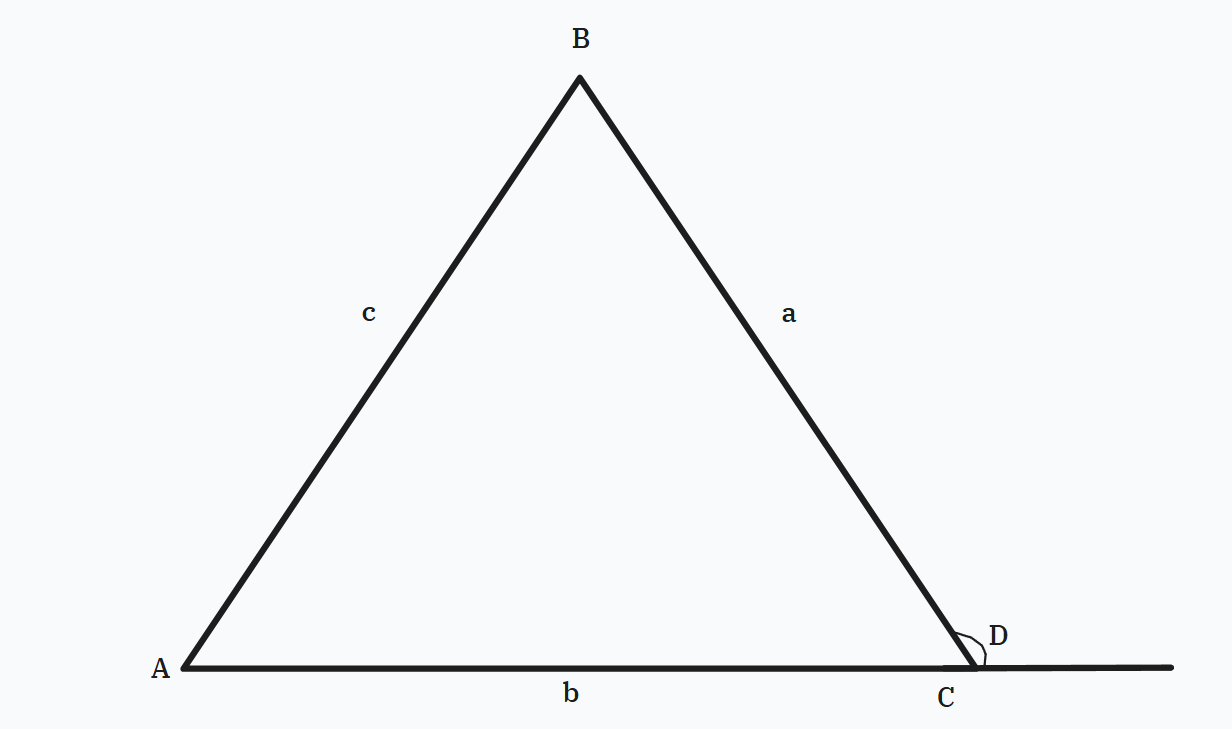
Figure 2: Triangle with angles (A, B, C) and exterior angle D.
-
Triangle Inequality Theorem:
The sum of any two sides is greater than the third side:
,,
-
Area of Triangle (basic):
In Figure(2), base = AC, and height = BD
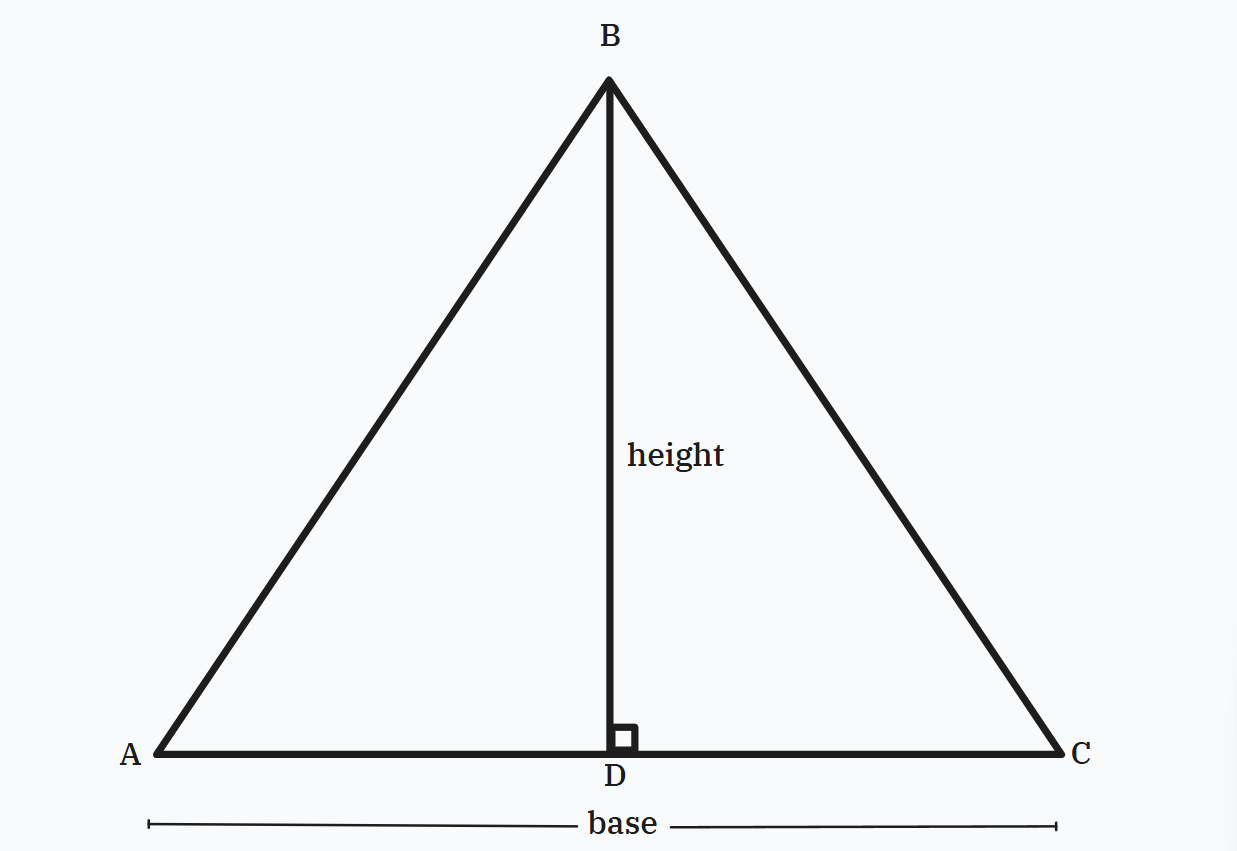
Figure 3: Triangle with Base (AC), and height (BD).
Base and HeightBase Height: Any side can be taken as base, but the Height is perpendicular to the base and touches the opposite vertex.
Types of Triangles
By Sides:
-
Scalene Triangle: All three sides and all three angles are different.
-
Sides: a, b, c (all distinct)
-
Perimeter:
-
Area (Heron’s formula): let , then
-
-
Isosceles Triangle: Two sides equal and the base angles equal.
-
Sides: equal sides and base
-
Base angles are equal; vertex angle is opposite the base.
-
Perimeter:
-
Height from the apex to base:
-
Area:
-
-
Equilateral Triangle: All sides equal and all interior angles are .
-
Side: (all three sides equal)
-
Angles: each
-
Perimeter:
-
Height:
-
Area:
-
By Angles:
-
Acute Triangle: All angles <
-
Right Triangle: One angle =
-
Obtuse Triangle: One angle >
Relationship Among Sides and Angles
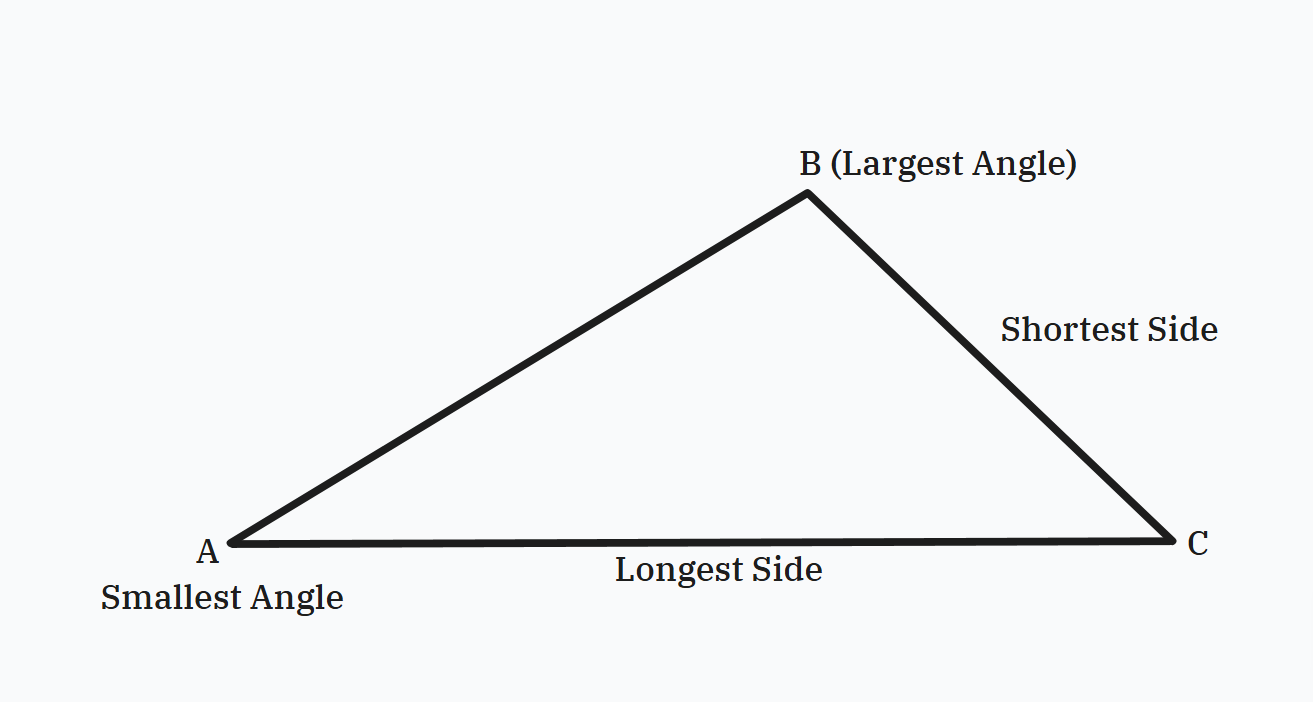
Figure 4: Triangle with variable length of sides.
-
Longest side is opposite the largest angle
-
Shortest side is opposite the smallest angle
Pythagoras Theorem (Right Triangle):
Where, is the hypotenuse,
is the Perpendicular ( Opposite ), and
is the Base ( Adjacent )
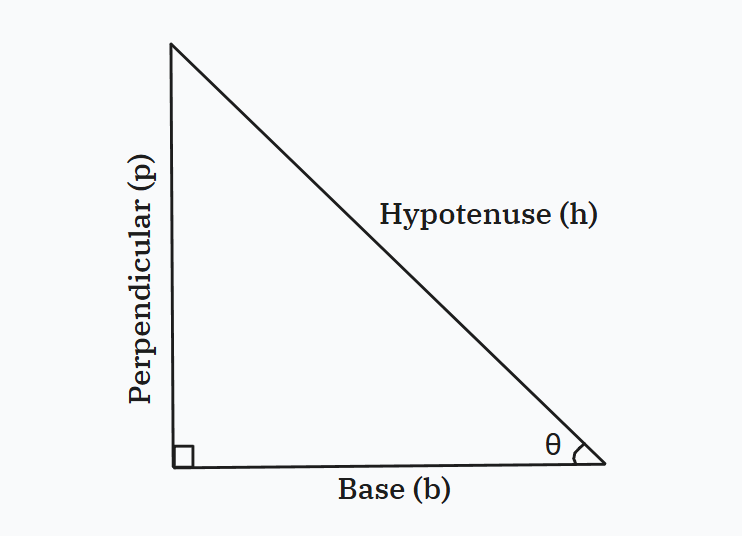
Figure 5: Right Angled Triangle.
Similar Triangles
Definition:
Two triangles are similar if:
-
Their corresponding angles are equal
-
Their corresponding sides are in the same ratio
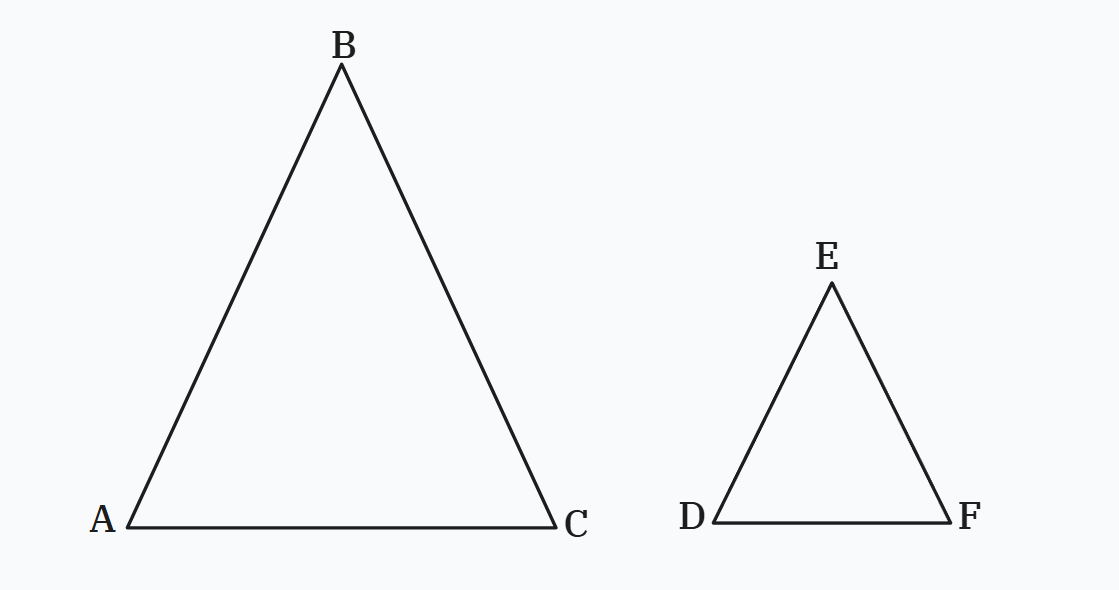
Figure 6: Two similar triangles.
Symbol:
Conditions for Similarity:
-
AA (Angle-Angle): Two pairs of equal angles
-
SSS (Side-Side-Side): All sides in same ratio
-
SAS (Side-Angle-Side): Two sides in same ratio and included angle equal
Properties:
-
Ratio of corresponding sides:
-
Ratio of areas:
Real-World Applications
-
Map scaling and model design
-
Shadow length problems
-
Architecture and trigonometry